Each object can have also an alternative state in addition to its normal state. By navigation between these two states object animations are created. The object may move, resize, rotate or change the density or orientation in space. Animations can be automatic when an object appears or it is controlled with push buttons.
If the object is set to automatic start, then the animation starts when displayed:
- if the object is part of paged article it starts by going to this page
- if the object is part of continuously scrolling article it starts at the moment when it is at least partially visible
- if the object is part of a variable object it starts by going to its state
Animations can also be automatically played back at the moment when the object disappears (the reader goes to another page, moves and switches the variable object.
Select the object (or group of objects) and press  button
button
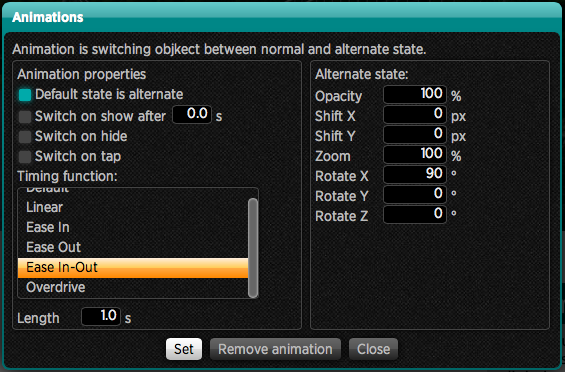
Set the animation properties on the left side of the window:
- Default state is alternate – means that at the beginning the object will be displayed in an alternative position (shifted, magnified, rotated, etc.) and later through the animation it will return to its normal state (thus as is illustrated in the editor). If this option is turned off, it will be just the opposite: the object will be illustrated in its normal position, as it was displayed in the editor, and later assumes the alternative state with animation
- Switch on show after 0.0 s – if checked, then object animation plays automatically after it is displayed, you can also specify the delay in seconds. This is suitable for example with flying headlines etc. At this time it will switch the object from an alternate to normal, or from normal to alternate state according to the above option
- Switch on hide – if checked, it will animate the object back when the object disappears from the display
- Switch on tap – the object itself will respond to touch. Beware of a collision with action setting on tap.
You can also set the object timing i.e. how it will move with time:
- Default – the default timing method, the object starts up quickly and before the end position slightly slows down
- Linear – object will move quite evenly from the beginning to end
- Ease In – object starts to move slowly and reaches the target position quickly
- Ease Out – object will move quickly but before the end position it slows down a lot
- Ease In-Out – object will slowly starts then speeds up the motion, before the end position it slows down a lot
- Overdrive – object starts very quickly, passes the end position and slowly returns back to the target position
The last option is to set the animation length in seconds. If you enter 0, then the object will not animate at all, but goes immediately from one state to another.
In the right part of the window you may then set what will be the alternative state of the object:
- Opacity – the saturation. If the object is set to its 100% saturation, and you make settings 0%, then the transition from an alternative to the normal state causes that the object appears.
- Shift X, Y – if the object has to come from the left, enter e.g.-300
- Zoom – normal magnification is 100% if you want to turn a small object into large one, enter 1%, if on the contrary, it should “drop” into the page, enter e.g. 500%. It is advisable to combine this state with saturation seeting.
- Rotate X, Y, Z – object rotation in space around selected axis:
- X – object rotates around an axis that is leading from left to right on the screen, i.e. if you enter 180 for example, it will appear “upside down“
- Y – object rotates around an axis that is leading from the top down, i.e. if you enter 180 for example, it will appear right-left inverted
- Z – object rotates about an axis perpendicularly to the face of your monitor, i.e. this turns inside of monitor plane. Remember that the target rotation may not always be 0 if you set the different editor rotation.
Press the button Remove animation to remove the animation.
Hint: You may control animated object by using the On tap command which acts as a button.